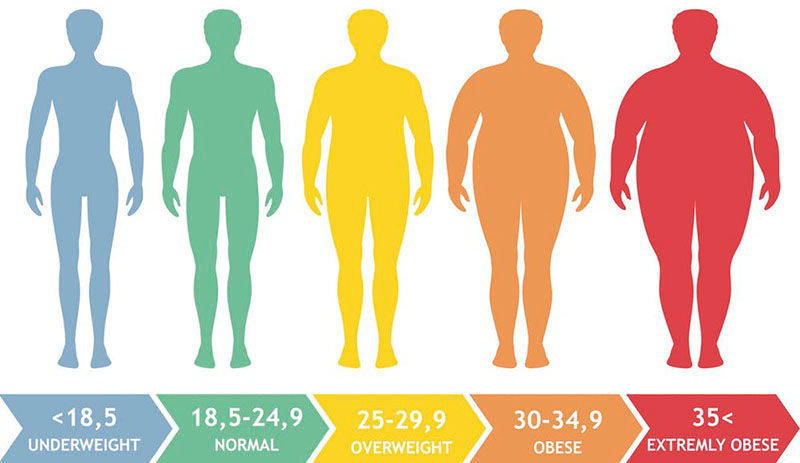
Obesity is a complicated condition characterized by an excess of body fat. Obesity is more than simply an aesthetic issue. It is a medical condition that raises the chance of developing other diseases and health issues, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and some malignancies.
Some people struggle to lose weight for a variety of reasons. Obesity is often caused by a combination of genetic, physiological, and environmental variables, as well as dietary, physical activity, and exercise decisions.
Causes
Genetics. Obesity is more likely to develop in a child if one or both parents are fat. Hormones involved in fat management are also affected by genetics. Leptin deficiency, for example, is one hereditary cause of obesity. Leptin is a hormone that is generated in fat cells as well as the placenta. When the body's fat levels are too high, leptin signals the brain to eat less. If the body is unable to create enough leptin, or if leptin is unable to tell the brain to eat less, this control is lost, and obesity ensues. The role of leptin replacement therapy as a treatment for obesity is being investigated.
Physical inactivity Sedentary folks burn fewer calories than active people.
Simple carbohydrates are abundant in the IQ diet. Carbohydrates' significance in weight growth is unclear. Carbohydrates raise blood glucose levels, which drive pancreatic insulin secretion. Insulin stimulates fat tissue development and can lead to weight gain. Some scientists believe that simple carbohydrates (sugars, fructose, desserts, soft drinks, beer, wine, and so on) contribute to weight gain because they are absorbed more quickly into the bloodstream than complex carbohydrates (pasta, brown rice, grains, vegetables, raw fruits, and so on) and thus cause a more pronounced insulin release after meals. Some experts believe that increased insulin release contributes to weight growth.
Overeating- Excessive eating causes weight gain, especially if the diet is heavy in fat. Foods heavy in fat or sugar have a high energy density (for example, fast food, fried meals, and sweets) (a lot of calories in a small amount of food). Epidemiologic research has found that high-fat diets lead to weight growth.
Factors of psychology Emotions can impact eating patterns for certain people. Many people overeat in response to negative feelings such as boredom, grief, tension, or rage. While most overweight persons have no more psychological issues than normal-weight people, around 30% of people seeking treatment for major weight problems struggle with binge eating.
Diseases: Obesity is also influenced by diseases such as hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, polycystic ovarian syndrome, and Cushing's syndrome. Obesity can be caused by certain disorders, such as Prader-Willi syndrome.
Symptoms
Excessive body fat, especially around the waist
Breathing difficulty
Sweating excessively
Snoring
Sleeping problems
Moisture accumulation in skin creases causes skin issues.
Inability to accomplish simple physical chores that one could undertake readily before weight gain
Fatigue can range from minor to severe.
Back and joint pain, in particular
Negative self-esteem, despair, humiliation, and social isolation are all examples of psychological difficulties.

Comments